1 September 2022
Exercise intolerance post-COVID-19 appears to have multiple causes and is not solely due to deconditioning.
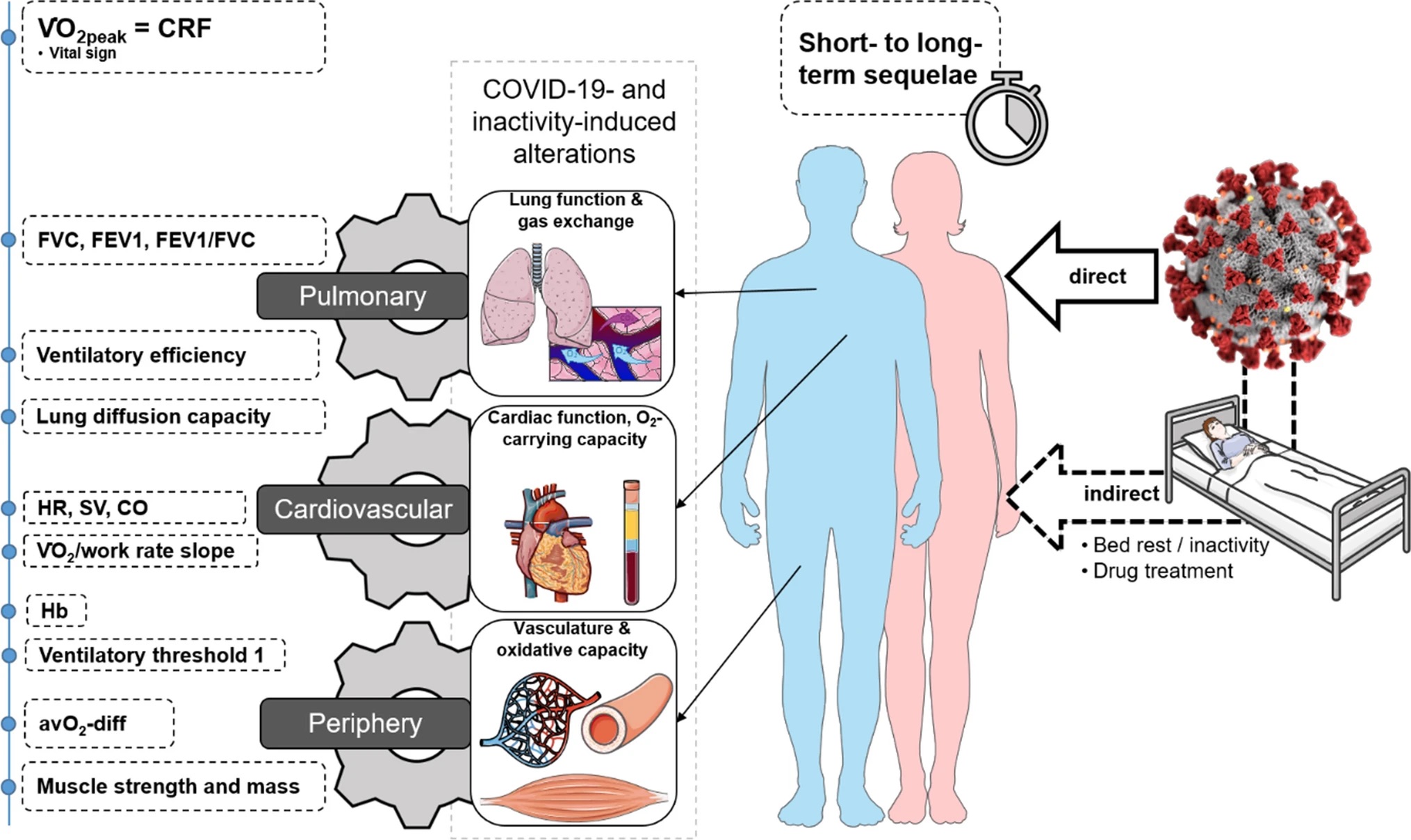
News, PublicationsThe recently published review article provides a detailed overview of existing studies looking at exercise intolerance and possible underlying mechanisms up to one year after disease onset. We were able to show that not only deconditioning, as claimed by many studies, but also peripheral followed by cardio-circulatory limitations as well as diffusion disorders of the lung are central to the long-term consequences of COVID-19. The article was published in Sports Medicine and is freely accessible there.
Publications